


Introduction: Fat transfer following breast reconstruction
Fat transfer following breast reconstruction allows breast specialists and surgeons to correct any prior breast contouring irregularities that remain following breast reconstruction.
Surgeons routinely perform breast reconstruction with implants following the removal of breast tissue in a mastectomy. Typically, they use a temporary implant known as an expander, which they inflate in a delayed manner to stretch the breast skin after cancer surgery has removed the breast tissue.
Once inflated, surgeons replace the expanders with permanent and much softer silicone implants. However, breast implant reconstruction with implants has limitations. Breast implants restore lost volume but do not fix contour irregularities from mastectomy dissection variations with round silicone implants.
This is where fat transfer becomes crucial. Fat serves as a malleable material, which is employed to address residual contour irregularities. Surgeons can harvest fat from any body part with undesirable fat deposits. Fat transfer following breast reconstruction significantly enhances your overall breast and body contour.
Breast reconstruction revision should be performed by trained breast specialists who are breast revision specialists. Breast surgery revision presents a unique challenge for surgeons as they are working on an unnatural canvas. The advantage of fat transfer following breast reconstruction is that it allows a plastic surgeon to fill in contour irregularities such as dents and divots that may be present.
The fat transfer gives the surgeon the flexibility to treat specific areas in the breast that are unachievable through breast implants.
Fat Transfer Following Breast Reconstruction Case Study
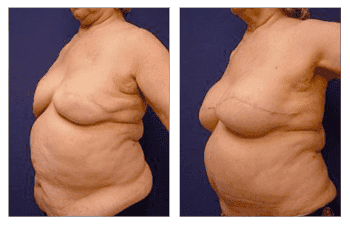
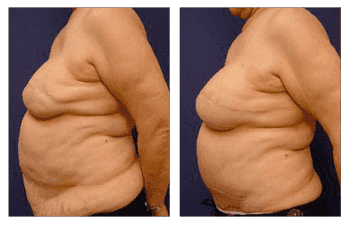
Our patient presents an example of a fat transfer following breast augmentation. She showed breast asymmetry after her original reconstruction surgery with implants and had various unevenness in each breast. Both breasts also showed signs of deflation. SurgiSculpt needed to utilize a fat transfer procedure using a closed-loop, pure graft system with VASER liposuction to treat both breasts independently.
This resulted in the correction of the deflated look in both breasts. She also shows improved breast symmetry and overall appearance regarding shape and fullness. Breast reconstruction and fat transfer on our 63-year-old female following bilateral breast reconstruction revision with implant replacement and fat grafting to improve breast shape.
Let us look at fat transfer in breast reconstruction in more detail.
Breast Reconstruction with Fat Grafting Details
Breast reconstruction with fat grafting involves several steps. First, fat is harvested from the patient’s own body through liposuction, typically from areas like the abdomen, thighs, or flanks. The harvested fat is then processed and refined to remove excess fluids and impurities, leaving behind pure fat cells. Next, the refined fat is carefully injected into the breasts to reconstruct and enhance their shape and volume.
Harvesting fat from the patient’s own body has the advantage of using natural tissue, reducing the risk of rejection or complications. It also allows for contouring of the donor sites, providing an added benefit of body sculpting.
Additionally, fat transfer in breast reconstruction can be used for various purposes, such as improving the appearance of lumpectomy defects, correcting asymmetry, or enhancing the results of implant-based reconstruction. Fat grafting can help create a more natural-looking and feeling breast, particularly in cases where there is insufficient tissue for implant placement or in combination with other reconstructive techniques.
Overall, breast reconstruction with fat grafting offers a safe and effective option for restoring a woman’s natural contours after mastectomy.
How Fat Grafting Works
Fat grafting, also known as fat transfer or fat injection, is a popular cosmetic procedure that involves removing fat from one area of the body and injecting it into another area to enhance volume and contour. This natural approach to augmentation has gained popularity due to its ability to achieve natural-looking results and its minimal risk of allergic reactions or complications. From the procedure to the recovery process, understanding how fat grafting works is essential for those considering this innovative technique for rejuvenating their appearance.
About fat injections
Fat injections for breast reconstruction offer several benefits, including a natural and soft appearance, minimal scarring, and the ability to contour the breast shape. The recipient site for fat injections is the breast area that requires reconstruction, where the fat is injected to improve volume and shape. The donor site is typically the abdomen, thighs, or buttocks, where excess fat is harvested through liposuction.
The procedure involves extracting the fat from the donor site, processing it, and then injecting it into the recipient site. This method allows for personalized and natural-looking results. Additionally, fat injections can be combined with breast implants to further enhance the reconstruction and achieve the desired size and shape.
Considerations for fat injections include the need for multiple sessions to achieve the desired results, as some of the injected fat may be reabsorbed by the body. Patients should also have sufficient donor fat for the procedure. Overall, fat injections for breast reconstruction offer a valuable option for achieving natural-looking results with minimal scarring.
METHODS
The patient classification and inclusion criteria for the autologous breast reconstruction study involved female patients who had undergone a mastectomy and were eligible for breast reconstruction using their tissue. The steps of breast reconstruction included tissue flap creation, microsurgical flap transfer, and shaping of the breast mound.
Informed consent was obtained from all participants, and institutional review board approval was obtained to ensure the ethical conduct of the study by the Declaration of Helsinki. A prospectively maintained database was used to collect and store patient information. The study was conducted at multiple medical centers, including (list of medical centers), from (time frame of study).
Anticipated Results
Fat grafting for breast reconstruction typically yields the anticipated results of improved breast volume, natural shaping, and scar improvement. The procedure involves transferring fat from one area of the body to the breasts, resulting in a more natural look and feel compared to traditional implants. Over time, the grafted fat cells integrate with the existing breast tissue, providing long-lasting results.
However, multiple procedures may be necessary to achieve the desired outcome, as the body may reabsorb some of the transferred fat cells. It is important for patients to have realistic expectations for the final result and be prepared for the possibility of undergoing additional sessions.
While fat grafting for breast reconstruction has many benefits, complications such as infection, cyst formation, and calcification may arise, leading to the potential abandonment of the method. Additionally, factors such as smoking, radiation therapy, and existing breast implants can also impact the success of the procedure and may necessitate alternative reconstruction methods.
In conclusion, fat grafting for breast reconstruction can provide improved breast volume, natural shaping, and scar improvement, but it is crucial to consider the potential need for multiple procedures and be aware of the potential complications and factors that could affect the success of the method.
Risks
Fat grafting for breast reconstruction carries several potential risks and complications. First, there is a risk of bleeding and infection at the grafting site, which can prolong the healing process and lead to further complications. Scarring and irregularities in the breast shape and texture may also arise post-procedure. Additionally, fat necrosis, the death of fat cells, can occur, causing lumps and discomfort in the reconstructed breast.
Long-term concerns include the possibility of unsuccessful grafting, leading to the reabsorption of fat and a decrease in breast volume over time. This can result in the need for additional surgeries to maintain the desired breast size and shape. Moreover, there are general surgical risks such as the formation of cysts, infection, calcification, and migration of fat cells, which may impact the appearance and health of the breast tissue.
It is important for individuals considering fat grafting for breast reconstruction to thoroughly discuss these risks with their healthcare provider and make an informed decision based on their specific circumstances.
Fat Reabsorption and How to Deal with It
After a fat transfer procedure, some of the transferred fat may be reabsorbed by the body. The process of fat reabsorption occurs naturally as the body metabolizes the fat cells. To address fat reabsorption, patients have the option of undergoing an additional fat transfer procedure to add volume and maintain the initial results. This involves harvesting fat from another part of the body and injecting it into the desired area.
Recovery steps for dealing with fat reabsorption include wearing elastic bandages to reduce swelling and support the surgical area, taking pain relievers as prescribed by the surgeon, and avoiding pressure on the breasts to allow for proper healing. Patients can expect to see improvement in the appearance of the treated area over a few weeks, with full results becoming apparent within a few months.
In the case of fat reabsorption, it is important to consult with the surgeon to discuss the option of additional fat transfer and to follow the prescribed recovery steps for optimal results.
After your fat grafting procedure
fter your fat grafting procedure, it is important to understand the recovery process and what to expect. Swelling and bruising are common side effects and can last for a few weeks. Discomfort and tenderness in the treated areas may also be experienced. It is important to avoid strenuous activities and heavy lifting during the initial recovery period.
In some cases, a compression garment may be recommended to minimize swelling and provide support to the treated areas. A post-operative bra may also be necessary for added support and comfort. The timeline for returning to work may vary depending on the individual and the extent of the procedure, but typically patients can expect to go back to work within 1-2 weeks.
Factors that make a person a good candidate for fat grafting include breast size asymmetry, the need for volume in specific areas such as the breasts or buttocks, and previous surgical procedures that may have resulted in volume loss. It is important to consult with a qualified plastic surgeon to determine if fat grafting is the right option for your specific needs and goals.
Recovery from Fat Grafting for Breast Reconstruction
After fat grafting for breast reconstruction, patients can expect to experience swelling and discomfort for the first 1-2 weeks. It is important to avoid putting pressure on the breasts during this time, and patients should refrain from any strenuous activities or heavy lifting for at least 4-6 weeks. Light exercise can be resumed around the 3-4 week mark, but patients should consult with their surgeon before doing so. Most patients are able to return to work within 1-2 weeks, depending on the nature of their job.
Swelling and soreness in the donor sites, where the fat was harvested, can last for several weeks. Patients can expect to see improvement in swelling and discomfort over the first few weeks, but it may take 6-12 months for the final results to be fully apparent. Following the post-operative care instructions provided by the surgeon, including wearing any recommended compression garments, can help minimize swelling and discomfort.
Overall, the recovery from fat grafting for breast reconstruction can vary for each individual, and it is important to follow the specific recommendations provided by the surgeon to promote optimal healing.
Benefits of Breast Reconstruction Using Fat Grafting
reast reconstruction using fat grafting offers numerous benefits. Unlike traditional implant-based reconstruction, fat grafting uses the patient’s natural tissue, resulting in a more natural look and feel. This technique also allows for better shaping and contouring of the breasts, providing a more aesthetically pleasing result.
Fat grafting can also address scarring and create symmetry in cases where there is a significant difference in breast size or shape. It is an effective option for correcting tuberous breasts and natural asymmetries, producing more balanced and symmetrical results.
Furthermore, fat grafting can reduce post-operative pain compared to other reconstruction methods, as it involves minimal incisions and avoids the use of implants. Additionally, the results of fat grafting are long-lasting, offering a more permanent solution for breast reconstruction.
In conclusion, breast reconstruction using fat grafting offers the advantages of natural tissue, improved shaping, reduced pain, long-lasting results, and the ability to fix scarring and create symmetry. This technique provides a viable option for patients seeking natural-looking and symmetrical breast reconstruction.
The Science and Techniques Behind Fat Grafting
Fat grafting, also known as fat transfer or fat injection, is a cosmetic surgical procedure that involves harvesting fat from one part of the body and injecting it into another to add volume or reshape the area. The science and techniques behind fat grafting involve the intricate understanding of the properties of adipose tissue and the meticulous handling of the harvested fat.
This innovative procedure has gained popularity in plastic surgery due to its natural and long-lasting results, making it a preferred option for facial rejuvenation, breast augmentation, and body contouring. Understanding the scientific principles and mastering the techniques of fat grafting are essential for plastic surgeons to effectively perform this procedure and achieve desired aesthetic outcomes for their patients.
Where Does the Fat Come From?
Fat transfer for breast reconstruction involves the removal of fat from one area of the body and transferring it to the breasts to enhance their shape and volume. The donor sites for harvesting the fat can include the belly, thighs, or flanks (love handles).
The process begins with the extraction of fat from the donor site using a gentle liposuction technique. This technique ensures that the fat cells remain intact and undamaged during the harvesting process. The collected fat is then processed to purify it, isolating highly enriched stem cells that aid in the healing process and enhance the final results of breast reconstruction.
The purified fat, containing concentrated stem cells, is then carefully injected into the breast tissue to achieve the desired shape and volume. These stem cells help promote tissue regeneration and improve the overall cosmetic outcome of the reconstruction.
In conclusion, fat transfer for breast reconstruction utilizes fat from donor sites such as the belly, thighs, or flanks, and through a meticulous liposuction technique, processes the fat into pure fat containing highly enriched stem cells to aid in the healing process and enhance the final results.
How Does Fat Grafting for Breast Reconstruction Work?
Fat grafting for breast reconstruction involves the transfer of fat from one part of the body to the breast area to create a more natural and full appearance. Post-lumpectomy fat grafting involves injecting the harvested fat into the breast to improve its appearance after the removal of a portion of the breast tissue. Post-mastectomy fat grafting, on the other hand, is used to recreate a natural-looking breast mound after the entire breast has been removed.
During a secondary surgery, fat is injected into the breast in multiple small deposits to achieve a natural and soft feel. The procedure allows for the sculpting and shaping of the breast to improve symmetry and appearance.
Benefits of fat grafting for breast reconstruction include making the reconstructed breast feel soft and natural, improving the appearance and symmetry of the breast after lumpectomy and radiation, and reducing the need for implants or additional major surgeries. Overall, fat grafting for breast reconstruction can provide a more natural and aesthetically pleasing result, ultimately improving the physical and emotional well-being of the patient.
Ideal Candidates for Fat Grafting
Ideal candidates for fat grafting are individuals who have excess body fat in specific areas that can be harvested and transferred to another part of the body for volume enhancement. They should be in good overall health, with no history of severe illnesses or medical conditions that could impact the healing process. Candidates should also have realistic expectations about the results of the procedure and be committed to maintaining a healthy lifestyle post-surgery.
Physically, ideal candidates should have sufficient donor fat in areas such as the abdomen, thighs, or buttocks, and be at a stable weight. They should not be pregnant or breastfeeding, as these conditions can affect the results of the procedure. The types of fat grafting procedures, such as facial fat grafting and breast augmentation with fat grafting, have specific criteria based on the patient’s desired outcome and the area of the body being treated.
Overall, individuals who are in good health, have excess fat in certain areas and have realistic expectations are ideal candidates for fat grafting procedures.
Combining Implants and Fat Grafting
Combining breast implants with fat grafting in the context of breast reconstruction involves two main steps. First, a breast implant is placed to provide volume and shape to the reconstructed breast. This is followed by fat grafting, where fat is harvested from other areas of the body, such as the abdomen or thighs, and then transferred to the breasts to achieve a more natural contour and texture.
The benefits of using transferred fat to achieve a more natural breast contour and texture include improved softness, more natural movement, and a reduced risk of implant visibility or rippling. Additionally, fat grafting can help to improve the appearance of scars and provide a more natural transition between the implant and the surrounding tissues.
For some patients, multiple procedures may be required to achieve optimal results. Candidates for fat grafting are typically those who have undergone mastectomy for breast cancer, have insufficient tissue to cover the implant, or desire a more natural-looking reconstruction. Patients need to consult with a qualified plastic surgeon to determine if they are good candidates for this combined approach to breast reconstruction.
Conclusion: Fat Transfer Following Breast Reconstruction
In conclusion, fat transfer following breast reconstruction offers numerous benefits, including a more natural look and feel compared to traditional implants, the possibility of correcting contour irregularities, and the potential for additional improvement in overall body shape. The recovery process typically involves harvesting fat from areas such as the abdomen, thighs, or buttocks through liposuction, which may result in minor discomfort and swelling at the donor sites.
The timeline for recovery varies, but patients can expect to resume normal activities within a few weeks, with limitations on strenuous exercise for several weeks to allow for proper healing. Precautions during the healing process may include avoiding excessive pressure or trauma to the treated areas. Overall, fat transfer can provide long-lasting, natural-looking results for those undergoing breast reconstruction, with a relatively straightforward recovery process.
Breast reconstruction and fat transfer on 63-year-old female following bilateral breast reconstruction revision with implant replacement and fat grafting to improve breast shape.
