
Rapid recovery breast augmentation refers to the seamless recovery provided to patients who undergo breast enhancement surgery. Patients traditionally experienced moderate discomfort associated with the dissection of the tissues in the breast required to position a breast implant. This discomfort was a natural process of any surgery requiring surgical dissection.
Dissection will typically involve the disruption of microscopic sensory nerves that will emit the sensation of pain. In addition, bleeding in the tissues automatically releases pro-inflammatory products that trigger your pain nerves.
This is again a normal consequence of body safety mechanisms; for example, if you were to cut yourself, this is your body’s mechanism to inform you that you have cut yourself. However, discomfort following surgery is a side effect that most want to avoid. All desired pain-less breast augmentation surgery has been made possible by surgical design advances and coined rapid recovery breast augmentation.
Rapid recovery breast augmentation has been made possible following advances in surgical technique. The first is transitioning dissection of the breast tissues and subsequent implant pocket from above the muscle to below the muscle. This is because the plane under the muscle is free of tight attachments and described by a loose layer void of diffuse nerves and vessels. Instead, there are only two discrete nerve and vessel bundles, one located over the medial aspect of the chest and another less frequent over the lateral aspect.
In addition, for rapid recovery breast augmentation technique, a lighted mammary retractor is used to visualize the lighter dissection so that both of these bundles, when visualized, are protected. This means that in addition to not injuring any sensory nerves, not a single drop of bleeding is spilled. When bleeding is avoided, then no pro-inflammatory products contaminate the field.
Finally, using an ultrasound-assisted local anesthetic is injected into the nerve roots that travel in between the pectoralis major and minor muscles. In general, larger nerve trunks, called nerve roots, will travel in between muscle groups.
The main muscles in the chest include the major and minor pectoralis, and the interphase between these two muscles can be injected accurately using ultrasound-assisted guidance. Another advance is the injection of a specialized local anesthetic solution. Traditionally, the local anesthetic would last up to 8 hours maximum.
However, advances in local anesthetic allow us to use a local anesthetic placed into slow-release microspheres so that the numbing medicine can work for up to 4 days. Since the first three days following surgery are typically the hardest, you will have escaped the most difficult postoperative period.
Rapid recovery breast augmentation has been made possible through advances in surgical techniques and numbing medications. If you have been avoiding breast augmentation due to fears of postoperative pain, this is your time. If you have been desiring breast augmentation surgery but were afraid of discomfort, we invite you to consider rapid recovery breast augmentation that will provide you with a seamless recovery.
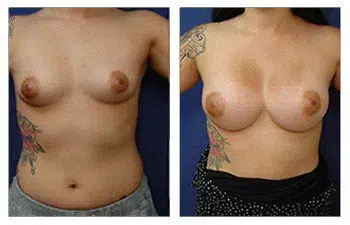
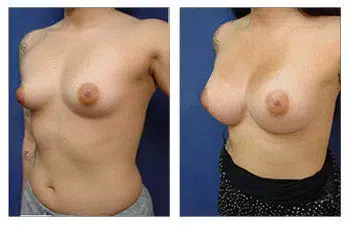
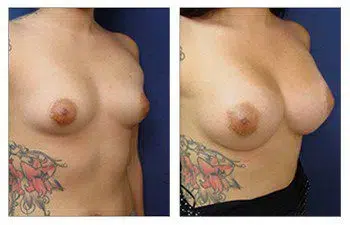
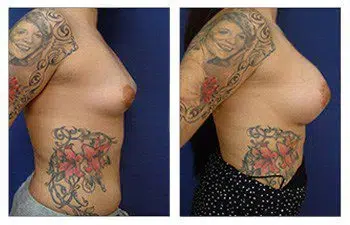
Please admire this 41-year-old female who completed her rapid recovery breast augmentation surgery.
