


Several considerations and maneuvers are utilized to avoid breast asymmetry during breast augmentation. The first consideration is identifying any preoperative asymmetries which not improved with a simple breast augmentation. The classic example is the nipple-areola malpositioning.
When there is nipple and areola malpositioning, the placement of an implant will only make this asymmetry more obvious. Another is breast mound asymmetry. Breast mound asymmetry must be identified before surgery so that breast mound asymmetry may be corrected by choosing variable breast implant sizes and styles. For example, let us consider two breast mounds that are asymmetric in size.
To correct the size discrepancy, a larger implant may be considered for the smaller breast mound side. Another consideration is breast shape asymmetry. Let us consider that one breast mound is narrower than the other. The narrower breast mound can be augmented with a wider implant than the other side by choosing a lower profile implant. As a result, breast mound dimensions must be measured accurately and comprehensively to guide choice in breast implant sizes and shapes.
The second consideration for avoiding breast asymmetry following breast augmentation is to be conscious of the nipple asymmetry. When the nipples are positioned asymmetrically, for example, if the breasts have variable sagging, a breast lift must be considered. The breast lift will not only help with nipple-areola symmetry but can also correct any breast mound asymmetry that cannot be corrected with implants alone.
The final consideration for avoiding breast asymmetry following breast augmentation is ensuring that breast asymmetry is not created on breasts that were symmetric to start with. The most common cause of breast asymmetry following breast augmentation performed on symmetric breasts is implant malposition.
Although implant malposition may occur in the postoperative period, most cases involve surgeon error. In summary, the most important maneuver to avoid asymmetry following breast augmentation in symmetric breasts is to ensure that breast implant pockets are created symmetrically.
The most critical component to ensuring implant pocket symmetry is using an inframammary approach for breast augmentation. Based on a survey of board-certified plastic surgeons, the inframammary approach to breast augmentation is associated with the lowest incidence of breast asymmetry nationally.
You might be wondering why this might be the case. It is because it provides the surgeon with the most visualizable means of assuring accurate pocket dissection and the best vector for assessing pocket symmetry. This is because a right-handed surgeon can stand on your right side and simultaneously position their hand into both pockets and visualize ideal symmetry.
If you are concerned about avoiding breast asymmetry following breast augmentation, we encourage you to schedule a consultation with SurgiSculpt.
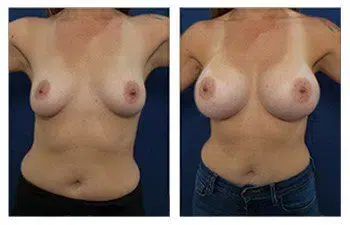
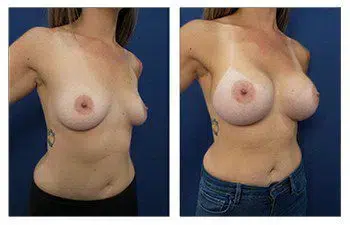
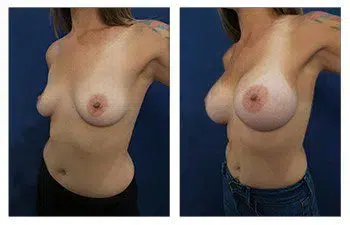
Please enjoy this 31-year-old who demonstrates perfect breast mound symmetry.
